Given all the hype and marketing push around IoT, it is tough to predict how exactly the business models will evolve over the next few years. This is one of the main concerns for industry practitioners. They usually ponder about implementing IoT and end up asking one question, “How can I use IoT in my industry?”. The common approach used to find answers to this question is to look at existing solutions. On one end of the spectrum, we have B2C solutions which are “good to have” ideas but do not solve a real pain. But on the other end, we see a few B2B trends around specific industries where IoT can play a pivotal role. The telecom sector is one such vertical and deploying IoT for telecom opens up a few interesting opportunities.
IoT Opportunities for Telecom
In this post, we present to you a few use cases from the telecom service provider vertical. Telecom has been the poster boy of high-technology industry for more than a decade. This is due to the rapid expansion, largely driven by innovation around internet and smartphones. Telcos have been capturing new geographies and promoting new services. All this adds complexity in optimally managing the network, combined with the thrust of launching new value-added services to thwart the competition.
The emergence of IoT presents a few interesting opportunities for telcos. The good news is that these opportunities can drive both the bottom line and top line, bringing in more operational efficiency as well as additional revenue streams. Let’s check out some of the available options.
IoT as a Tool for Improving Operational Efficiency
A significant portion of a Telcos’ operational cost is eaten up by remote infrastructure. It is where the original use case of IoT plays a major role, i.e. remote monitoring and management. Consider a cellular mobile operator network. Such a network will consist of a huge number of mobile cell towers distributed across a vast geographical area.
There are existing standards and protocols for managing telcos’ own remote equipment. But there are other issues. What about asset management, physical security, and environmental protection?
Asset Management & Monitoring
A remote cell tower site includes auxiliary equipment besides the main telecommunication equipment to make things work. A generator is one such component because power backup is an essential requirement for ensuring 24/7 network uptime. Air conditioning, UPS, energy meters are the other such vital assets. These are part of the passive infrastructure. Monitoring them for operational efficiency and predicting their failure in advance is an essential ingredient of remote management. IoT makes it possible.
Physical Security
Physical security is of paramount importance in remote places where there is costly equipment installed.
An IoT-enabled intrusion detection system is a must. Added to this, there are pilferable consumables like fuel and batteries used in the site. Hence we also need a resource consumption tracking system to ensure timely alerts to minimize losses.
Environmental Protection
Remote sites are always under the threat of being vandalized by the elements. Constant hazards in the form of fire, water, and air are a major challenge. IoT can help in detecting such conditions, such as smoke, flooding, or weather conditions and can assist in issuing control commands to either take preventive measures or shut down the system to avoid irreparable damages.
IoT as a Service for Providing Last Mile Access to Devices
While we have stressed upon the use of IoT to manage remote telco sites, one thing to be noted here is that IoT itself relies on a reliable communication link. And therefore, it is imperative to consider something which does not suffer from the drawbacks of the telco’s own terrestrial link failure.
Satellite Links
One possible option is a satellite link. This kind of service is provided by Vodafone in association with Immersat. If deployed for telcos’ remote sites, this obviates the need for sharing the terrestrial communication link, which in the case of failure, will also render the IoT system ineffective.
Low Power Radio
Telcos can also tap into the Machine to Machine(M2M) ecosystem by playing the service provider role. Unlike human to human communication which requires higher bandwidth and quality of service, M2M communication requires extremely low bandwidth. Traditionally we have tried to use the existing technologies such as GSM and WiFi to enable M2M communication. These high bandwidth-centric technologies are overkill for M2M. They are also power guzzlers and hence are not energy efficient in case of battery powered applications. Thus, in recent years, new standards have been developed for low-power, radio-based, wide area technologies which are optimized for low data rates, commonly known as LPWAN (Low Power WAN). These are extremely power efficient. Two such competing standards are NB-IoT and LoraWAN.
LoRaWAN has already taken up in some parts of the world. Typical use cases are in agriculture where we need to establish communication links with the sensors installed on the field. Similarly, in urban areas, LoRaWAN can be deployed for enabling public utilities such as parking systems.
Telcos have the opportunity to tap onto LoRaWAN by offering LoRaWAN services to businesses. Tata Communications Limited has already shown the way by adopting LoRa technology to be deployed across India to provide last mile IoT connectivity.
IoT as an Application for Delivering Intelligent, Value-Added Services
Being an IoT last mile connectivity service provider opens up new revenue streams for the Telcos. This offers a few new exciting avenues for the telcos, just like the way in which value-added services boosted basic telephony and mobile services.
Merging of Physical and Virtual Worlds
What if we could seamlessly find our way from virtual to physical world and vice versa. This concept is similar to the Physical Web proposed by Google. But Google’s approach works only in a PAN(Personal Area Network) space.
ProSe (Proximity Sensing) is a standards-based implementation of a service on top of 4G LTE cellular service which allows two devices to detect their proximity and exchange data. Here are some practical use cases of this.
Finding Places

Consider that you are in a new city, and you need to locate the nearest bus stand or train station to go to another part of the city. If every bus, train, and public transport aggregation point within the city has a ProSe enabled device, then it can sync up with your smartphone’s ProSe service to present you with an interactive application which can help you find your way to the nearest point. Added to this, if you can communicate with those devices, then they can present you with information (bus, train timings, etc.) that can help you make quick decisions.
Finding People
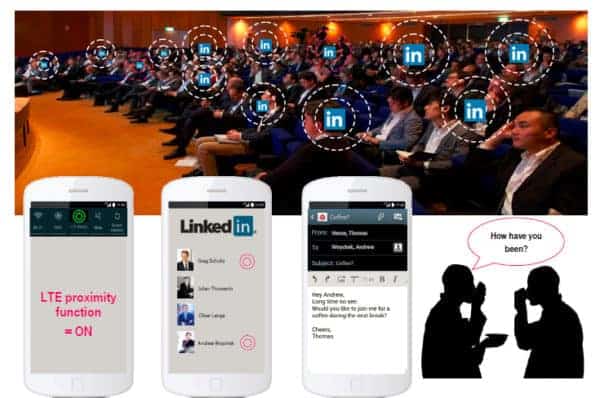
You are attending a conference and want to know if anyone within your Linkedin network is present there. If you and the others have enabled ProSe on their smartphones, then your LinkedIn app can quickly scan the people in your network who are nearby. It will then pop-up a list of people from your Linkedin network on your screen.
On-the-Go Collaboration
This is yet another interesting use case of PreSe and adapts well to our urban lifestyle. Imagine this. You have to catch a flight and are looking to book an UBER to the airport. But with ProSe you have yet another option. Just enable ProSe on your phone and scan your neighborhood. The chances are that there is someone who is also planning to go to the airport and then you guys can pool together. You can leverage this even if you are taking your car out to go somewhere. You can advertise your route through ProSe and set the terms and conditions for anyone to hitch a ride.
Machine to Machine Collaboration
If people can find places and other people, then what is stopping the machines? After all, machines are also getting smarter. They can learn to collaborate with humans and interact with the environment.
So what can we do with this?
Imagine you are traveling in a self-driven car and you changed your mind to alter your destination. Now your car needs to make a detour, for which it needs to change lanes. It can signal a “lane change” message to the other cars in the vicinity so that they can yield and allow it to do so. LTE-V is one such initiative under the ambit of 3GPP which is building a vehicle to vehicle communication protocol. This can enable vehicles to talk to each other and also the pedestrians and road infrastructure on the go. The use cases are many. Emergency braking notification, forward collision warning, hazardous location/intersection warning and many others.
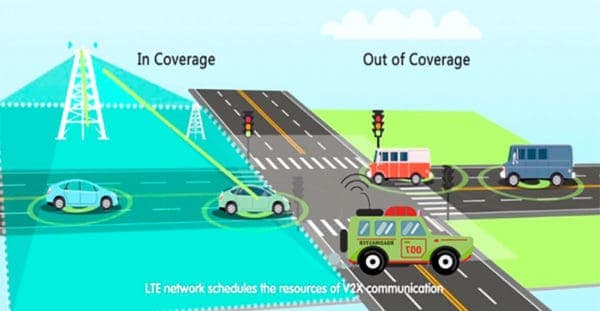
Huawei and Ericsson are leading the effort towards the standardization of LTE-V. You can find some more info about LTE-V here
The Next Move
While monitoring, control, and analytics, make-up the most obvious use cases of IoT, there is a new trend emerging. We are seeing a new wave of collaborative applications where the physical world can merge into our virtual lives enabling us to make a transition from virtual-to-physical or physical-to-virtual world seamlessly. And all this is happening in collaboration with smart things & intelligent devices. Over the next few years, this is a going to metamorph into an interconnected, intelligent world for humans and machines. That is where telcos can play a role by not only offering basic connectivity but also intelligent, value-added services. They have already taken the next move, and the future is going to be exciting.


