In this second part of "15 Mins with 5G" we will start looking at the 3GPP specifications for 5G network architecture and learn how to refer the specs. We will also cover 5G deployment scenarios from the specs as well as some of the informative web resources.
Check out this video for the 2nd 15 Mins with 5G session with Imtiyaz Ali. And just in case you missed it, you can also check out the 1st 15 Mins with 5G session.
Meandering the 5G Specifications
Reading the specifications have certain challenges.
- 3GPP Specification are Interlinked
- 3GPP Specifications Do Not Cover Examples
- Some Specifications Are Very Big - Eg, RRC 1000 Pages
- So Many Technologies Involved (UMTS, GSM/GPRS/EDGE, HSPA, IMS, LTE), and their terminologies makes it intimidating.
Three Key Stages in Following Specifications
1
Skimming - Get a general overview of the spec2
Scanning - Find a specific information, based on keywords or ToC3
Highlighting - Follow what you read and leave a trace
Rule of Thumb
- Know What You Want To Read
- Study The Respective Specification First Then Go to the References
- Follow What You are Studying
- Create Your Own Examples
- Take a Printout When Necessary (Not recommended)
5G Deployment Scenarios
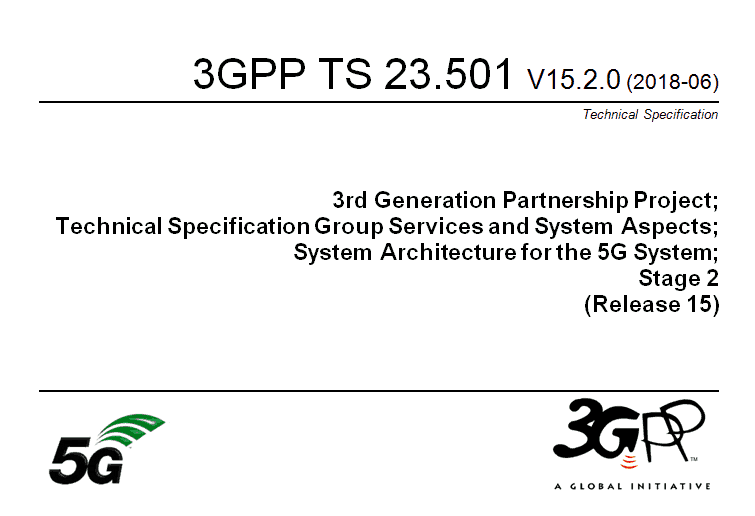
#1 - Homogeneous Deployment
- LTE cell and NR cells are overlaid and provide the similar coverage
- Both LTE and NR are macro cells
- NR is operating in the same band as LTE
- Cells are co-located cells
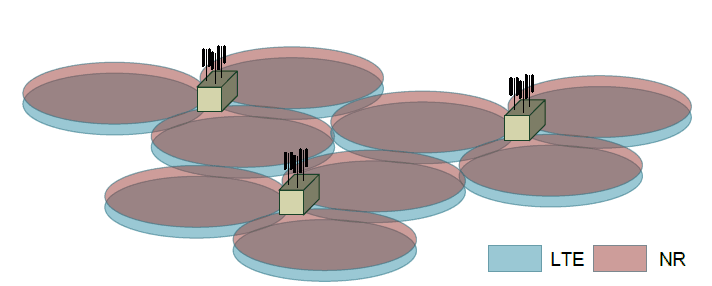
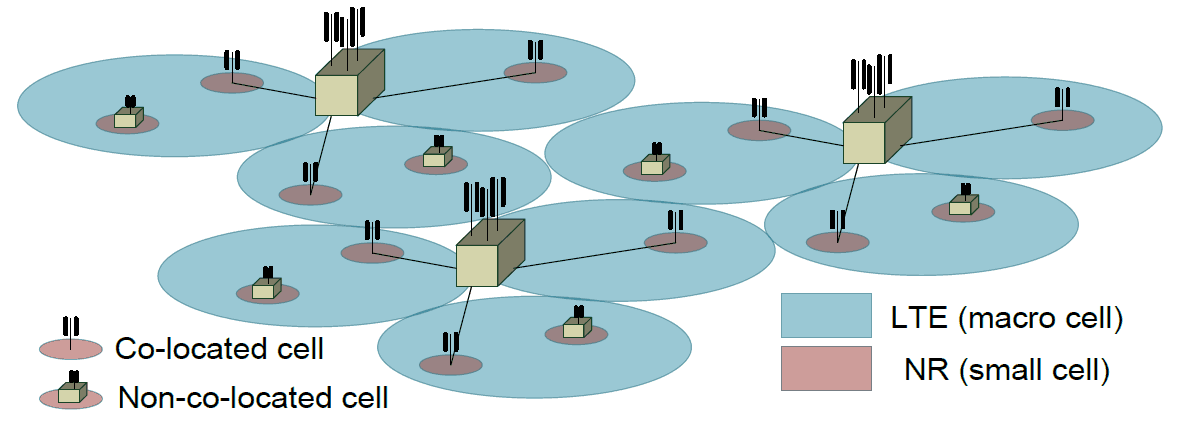
#2 - Heterogeneous Deployment
- LTE and NR cells are of different size
- LTE cell is large cell size - coverage requirement
- NR cell size is small - capacity requirements
- NR cell can be deployed as a co-located cell or a non-located cell as a hot spot
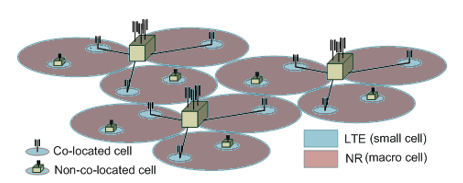
#3 Heterogeneous deployment
- LTE and NR cells are a different size
- NR cell is large cell size - coverage requirement
- LTE cell size is small - capacity requirements
- NR cell can be deployed as a co-located cell or a non-located cell as a hot spot
Core Network RAN Deployments
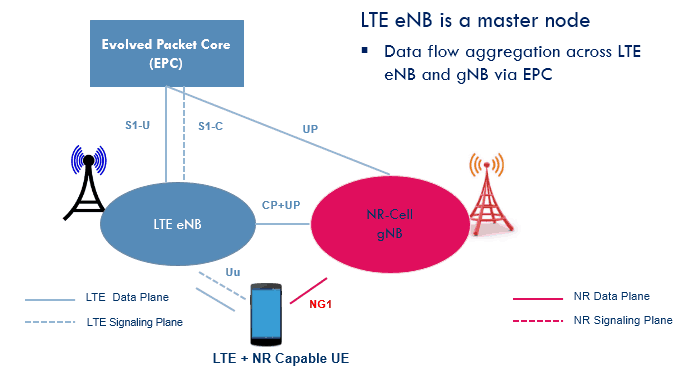
- Most famous for the Phase 1 non-standalone deployments
- LTE eNB will be master and anchor the NR cell
- Signaling procedure shall be done at LTE cell
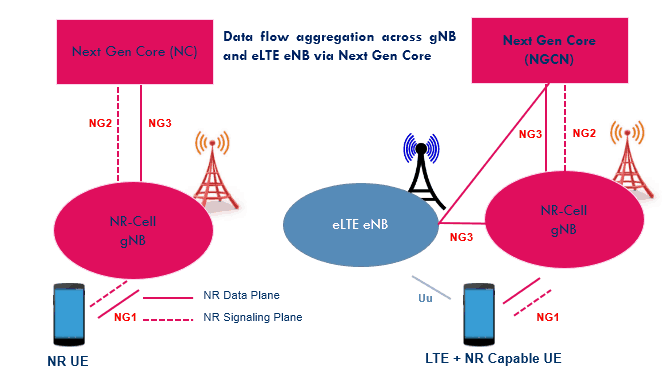
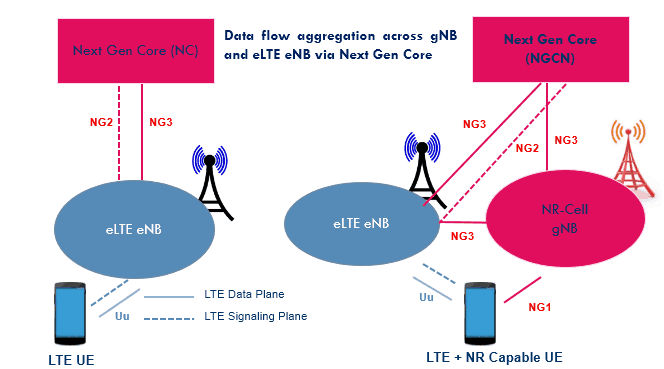
- Phase 2 where NR cell shall have stand-alone operational capabilities
- Anchoring the eLTE eNB
- Signaling procedure shall be done at NR cell
- eLTE eNB shall have capabilities to communicate with Next Gen Core network
- Release 14/release 15 LTE cell can be considered as eLTE eNB
- eLTE cell can be deployed standalone with Next Gen Core or eLTE eNB connected with Next Gen Core anchoring a non-stand alone NR cell
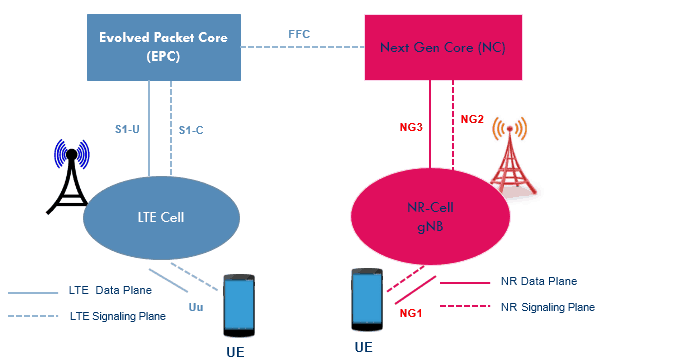
Individual RAT with Inter Mobility
- LTE and NR Radio access network are connected to their respective Core network
- Operated in a standalone environment and supporting mobility for LTE to NR cell and visa verse
- In phase 2 , when NR is capable to work as a standalone cell
- Interwork with WLAN for Wi-Fi offloading
- Utilize the benefits of the unpaid spectrum
Existing LTE Capabilities
5G radio offers downlink data throughput up to 20Gbps and uplink data throughput up to 10Gbps. Some of the interfaces in EPC are capable of handling (encode/decode) 5G throughput ranges
LTE Protocols & Interfaces | |
|---|
| |
| |
GTP-v2 interfaces - S5/S8/S10/S3 | |
| |
| |
Note: New AVP (Attribute Value Pairs)/IE(Information Elements) have been introduced in S6a, Gx , S1-AP and NAS to support 5G.
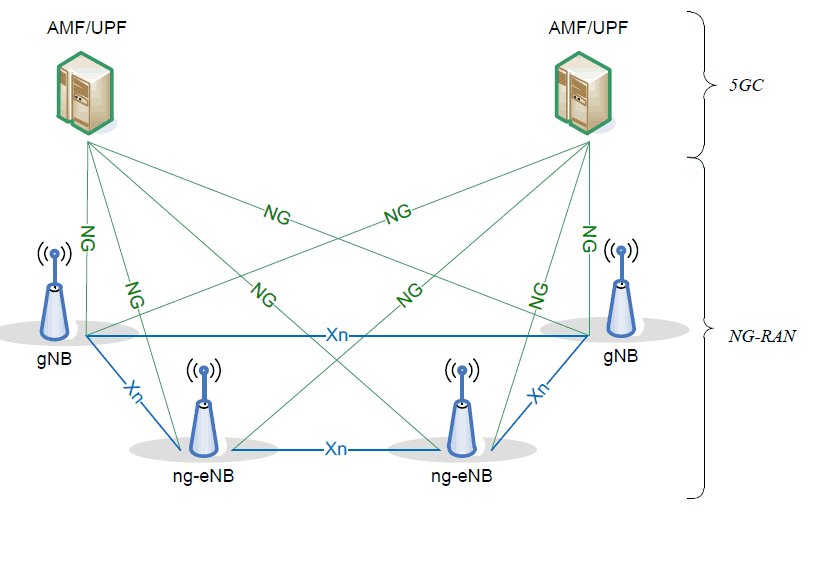
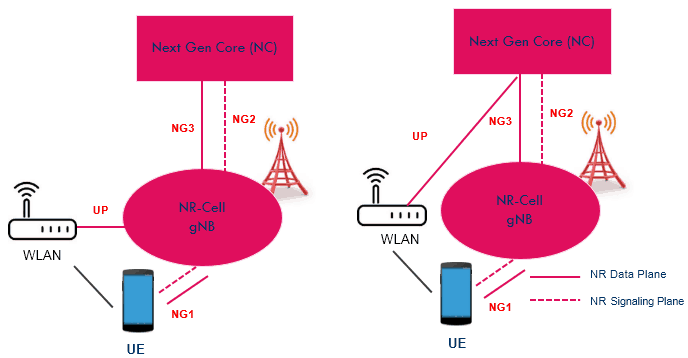
5G Radio Network Architecture
In 5G, the RAN node is referred to as the Next Generation RAN (NG-RAN). Radio Access Network (RAN) node connects to the UPF and AMF
The NG-RAN node is either a gNB or a ng-eNB, as follows
- gNB provides NR user plane and control plane protocol terminations towards the UE
- ng-eNB provides E-UTRA user plane and control plane protocol terminations towards the UE
The gNBs and ng-eNBs are interconnected with each other by means of the Xn interface
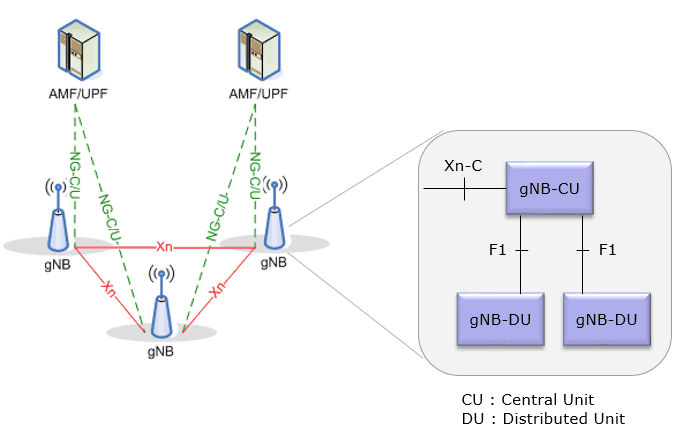
Central Unit (CU)
- Logical node - gNB functions like Transfer of user data, Mobility control, Radio access network sharing, Positioning, Session Management
- CU controls the operation of DUs over front-haul (Fs) interface
- Central unit (CU) may also be known as BBU (BaseBand Unit)
Distributed Unit (DU)
- Logical node - subset of the gNB functions, depending on the functional split option
- Its operation is controlled by the CU
- Distributed Unit (DU) also known with other names like RRH (Remote Radio Head)
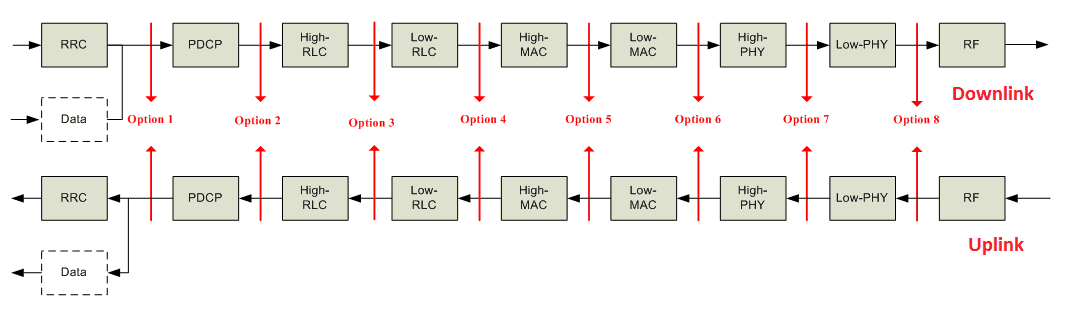
Central Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit(DU) Functional Split Options
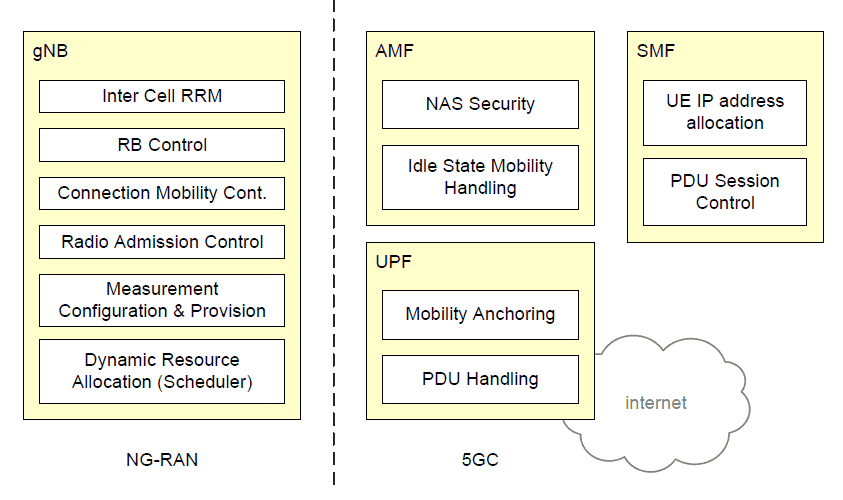
Functional Split - NG-RAN and 5G Core
5G CORE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
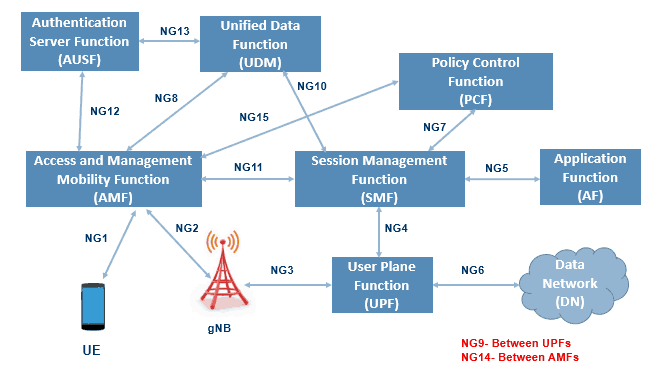
5G System architecture - Reference point representation
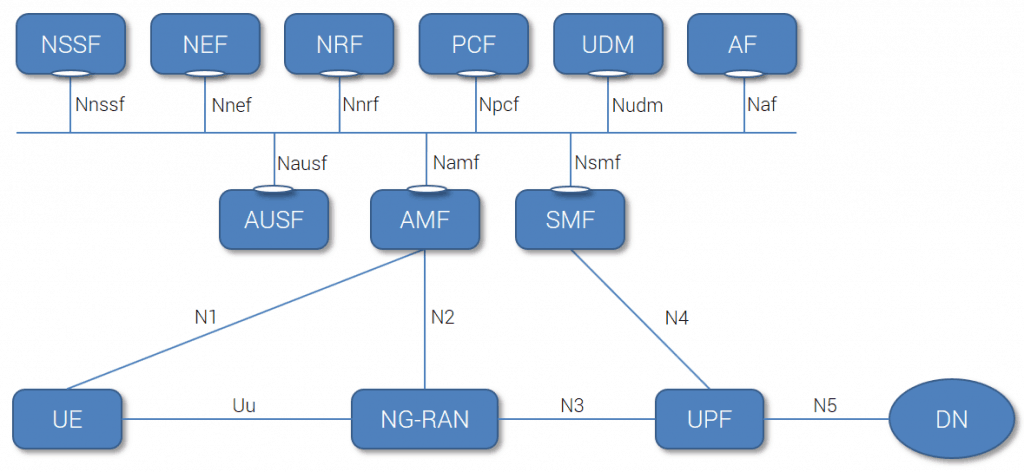
5G System architecture - Service-based representation
References


Very well described and looking forward for your next video …