IoT Security is at the center of most debates around IoT. Due to the spate of recent attacks, most discussions on IoT solutions invariably tend to deviate towards ensuring security in the system. And indeed, there seems to be an influx of more research papers about IoT security than IoT itself.
More...
All these trends point to only one thing. IoT security is indeed a cause for concern. The bad news, however, is, that from a product development perspective, security still is considered as a last point checklist to validate the product. In the absence of clearly defined regulations and incentives, there is a continued struggle for the companies to invest in security influenced design and development process right from the inception.
But the good news is, there is hope. At least in the form of alternative emerging technologies that are driving the future innovation in technology, in parallel with IoT. And this is evident in the recent publications of research papers that are bringing out new and ingenious ways of tackling the various challenges related to IoT security.
Let’s look a some of these emerging technology trends that will pave the way for a better and more secured Internet of Things deployment in the near future.
1. Blockchain
Blockchain is already being considered as a panacea for all security and accountability related issues faced by multiple industries. The inherent security features of Blockchain makes it an ideal choice for implementing various security measures in IoT. From data security, to managing authorizations and device identification, Blockchain is being imagined as the middleware security layer for IoT systems. Many of these ideas are in the research phase, and some initial implementations exist.
But there are bound to be challenges along the way, Especially when it comes to a huge distributed Blockchain ledger like the case of Bitcoin. The amount of time and processing power to mine a Bitcoin just keeps going up as the ledger expands. So it remains to be seen how will this impact large-scale IoT deployments. There are also some interesting implementations of Blockchain, like IOTA which proposes a "block less" chain. It aims to counter these scaling up issues faced by Bitcoin and become the de facto transport access layer for all IoT devices.
So we are going to see a lot of Blockchain use cases around IoT. This space is surely going to get very exciting in the coming years.
Wondering What Really Is Blockchain?
For a bare-bones overview of what essentially is a Bitcoin & Blockchain, here is a quick read covering the basics, courtesy coincentral.com
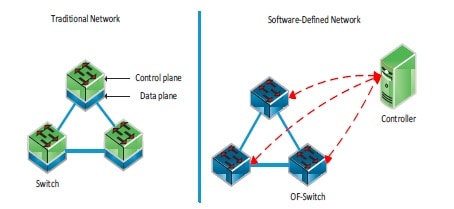
2. Software Defined Networking (SDN)
Software Defined Networking is making waves across the networking technologies for the last several years. A seemingly simple concept of separating the control plane of a router from its forwarding plane creates new possibilities in organizing and managing a large scale computer network. Most importantly, it also offers flexibility in custom deployment for different kinds of services over the internet and intranet applications which could not be achieved in the realm of traditional networking technologies.
With the threat of large scale DDoS attacks looming over the Internet and orchestrated through a huge army of compromised IoT devices, there is a lot of research going on in the areas of early detection of such attacks. SDN can possibly offer a solution to this. The SDN controllers which administer a network domain can communicate with SDNi, a set of specifications that enable Inter SDN controller communication. By exchanging information through SDNi, the neighbor SDN controllers can gauge some early warnings signs about an imminent DDoS attacks targeting computers in their neighborhood. This can immensely help network administrators to take corrective actions in time to mitigate the further propagation of attacks.
3. AI & Big Data
Big Data is already being used for recording incidents and analyzing anomalies in a network. And since AI chews all that big data, it can be fine-tuned for prediction of possible security breaches. In the telecom world, anomaly detection of CDR data is a well known technique employed by Telcos to guard against suspicious network activity. Similarly, networks connecting IoT devices can also track some metrics which directly reflect the utilization, bandwidth consumption and occurrence of certain events.
A big data repository of such metrics can be leveraged to run machine learning models for conducting periodic audit of networks for possible IoT security breaches. We have seen Google and other online services employing such measures to authenticate user access to their services. If you remember Google asking you for your location, or confirming your account through an OTP, then you know whats happening behind the scenes. There is big data and AI at play which checks for any anomaly in user access, such as location change, too frequent logins or even periodic checks. Something in similar lines needs to be done for IoT devices as well.
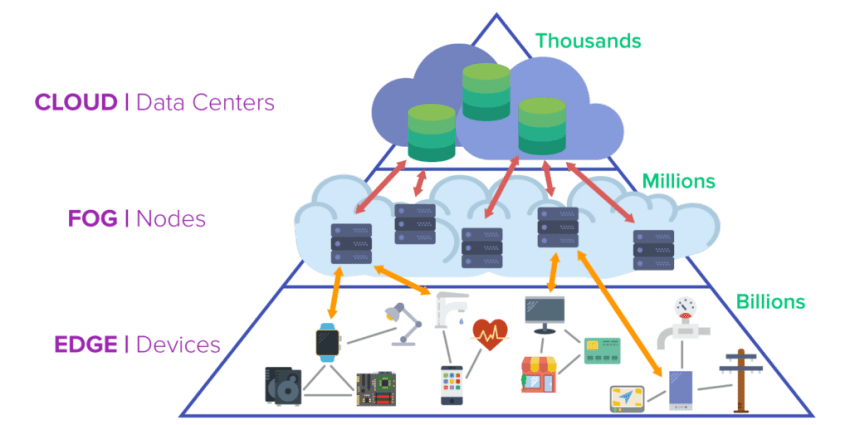
4. Edge Computing
Courtesy, erpinnews.com
More functions are moving from cloud to the edge, and IoT security strategy plays an important role in this transition. Gone are the days when the device capturing the data is responsible for storing and making it accessible. Under the newer paradigms of security management, the responsibilities of data capture are totally separate from data storage and data access. With more and more system functions getting deployed in the Edge, there needs to be a robust security framework to manage the data at the edge.
For IoT, this is also largely driven by the deployment of constrained devices. These are simple hardware devices which are low on processing capability, memory and run on a constrained environments that require low power consumption. There is a need to orchestrate secured access to these devices and the data generated from them. IETF has proposed a set of draft standards for this ( under the umbrella of CoAP specifications) and that calls for additional network elements in the IoT edge network to manage security aspects.
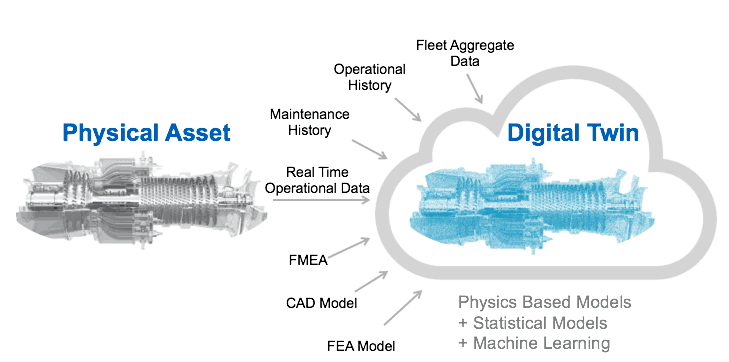
5. Digital Twin
Courtesy, www.geoilandgas.com
Since many IoT implementations comprise of constrained devices that may not be able to perform their own security functions, there is a need to rethink the security strategy for a mission-critical IoT deployment. One of the possible solutions is to think in terms of a Digital Twin.
A digital twin is a digital replica of a physical asset, and it can also extend to a group of assets that perform a closely orchestrated process, like in the case of an assembly line in a manufacturing plant. But a digital twin is not merely a replica that captures the states, properties or parameters of an asset. It goes much beyond and impersonates the physical thing in terms of its behavior and dynamic characteristics across the entire lifecycle of the asset. This way, a perfectly modeled digital twin of a mechanical spring could predict the time when the spring's tension will be reduced below the intended application.
A security breach also introduces specific behavioral and dynamic changes in an IoT system. If adequately modeled through a digital twin, there are immense possibilities for building a well guarded, defensive security system to thwart possible attacks. This concept is akin to a fly-by-wire system on a modern airliner which learns the prevailing flight & environmental situations and regulates the pilot's input based on that. A learned digital twin system can thereby regulate a malicious user input which might lead to an attack, either a physical attack on the assets or cyber attack on the IoT network connecting those assets.
Want to Know More About Trends In Digital Twins Technology in 2018 ?
Wondering if you could benefit from this amazing technology called Digital Twin? Check out this lucid summary, courtesy www.i-scoop.eu
The Way Forward
When it comes to ensuring basic cybersecurity measures, IoT is no different from the traditional internet and telecommunications networks. But there is a major paradigm shift in security design. And the key is "Separation of Responsibility".
So there will be additional layers, network elements and protocols added to an IoT network to manage security. And this will extend to all aspects of security, right from data to device and network and beyond, This could be good news for device manufacturers as they will be spared from guarding their data & devices on their own. But it remains to be seen, what are the more significant challenges that await us in the years to come as the pace of IoT deployment soars ahead? With more complex deployments and scale of device deployment and data syndication, things are difficult to predict right now, but surely it will be an exciting battle.