Voice controlled technologies are growing in popularity everywhere. From home automation to cab booking or ordering a meal, customers are getting pampered with the luxury of using voice to control things around them.
In this blog post, I present a tutorial to build a voice-activated Oxford dictionary using Amazon Alexa. You can talk to the dictionary and ask for definitions, example usage, synonyms or antonyms of any English word present in the Oxford dictionary.
Dictionary Bot – A Voice Controlled Dictionary Assistant
Often I stumble across some word from a classic English literature. I get hold of a dictionary, locate the word and then read the print in a tiny font. This can be irritating at times. And oh yes! I can Google for that word on my smartphone but then I run the risk of getting lost in the online world. Besides, none of these things really interact with me. What if I have a gadget to which I can literally ask about the word and it tells me the meaning and even example usage of that word?

This idea seemed fascinating to me and after a bit of research, I was able to successfully build a talking dictionary bot. The dictionary bot listens to my questions about meanings, synonyms, antonyms of any English word and gets answers straight from the definitive record for the English language – The Oxford Dictionary.
This blog post is an effort to document the building process of this dictionary bot. You can build one for yourself and enjoy this voice-controlled dictionary. You can even present it as a gift to your kids and help them expedite their learning of English language!
Introduction to Amazon Alexa
Alexa doesn’t really need an introduction. For those of you who don’t know, Alexa is a voice service from Amazon which provides a Voice User Interface (VUI) for you to interact with the world. Alexa can answer questions about weather, facts, history or play music, set alarm. You can access Alexa service with the hands-free smart speaker Echo or similar products from Amazon.
In addition, Amazon has put the power of Alexa in the hands of developers. To leverage the artificial intelligence behind Alexa, you develop a ‘skill’ to add more capabilities and features of your own to Alexa.
In this project, we will develop such a custom skill so that Alexa is able to retrieve and present you the information from Oxford dictionary for your query. If you are interested to know more about Alexa, here is a good information to start with.
[thrive_text_block color=”teal” headline=”Also Check Out This Home Automation Demo Built Using Alexa”]
Sometime back we used Alexa to build a voice-controlled home automation system. You can check out the post along with the complete build instructions, in two parts.
Voice Controlled Home Automation using Alexa – Part 1
Voice Controlled Home Automation using Alexa – Part 2
[/thrive_text_block]
Dictionary Bot Hardware
Amazon Echo is the device which comes to mind when you think of Alexa. However, that is not the only option to access Alexa voice service. You can get a feel of Alexa with some web based simulators such as echosim.io or you can run the service on a Raspberry Pi, if you belong to the ‘maker’ clan and enjoy DIY.
Co-incidentally I received a beta sample of ‘WisCore AVS Kit’ from RAK Wireless, a Shenzhen based company manufacturing a wide range of products to build IoT solutions. WisCore integrates Alexa Voice Service inside it, so you can use it almost out of the box to interact with Alexa. A companion mobile app lets you configure WisCore with your Amazon credentials and you are all set to experience the digital voice assistant. WisCore has several features and capabilities in addition to Alexa integration. You can find out more about WisCore and ordering information here.
For this project, WisCore is my choice for the hardware to power the dictionary bot.
The Dictionary Bot Architecture
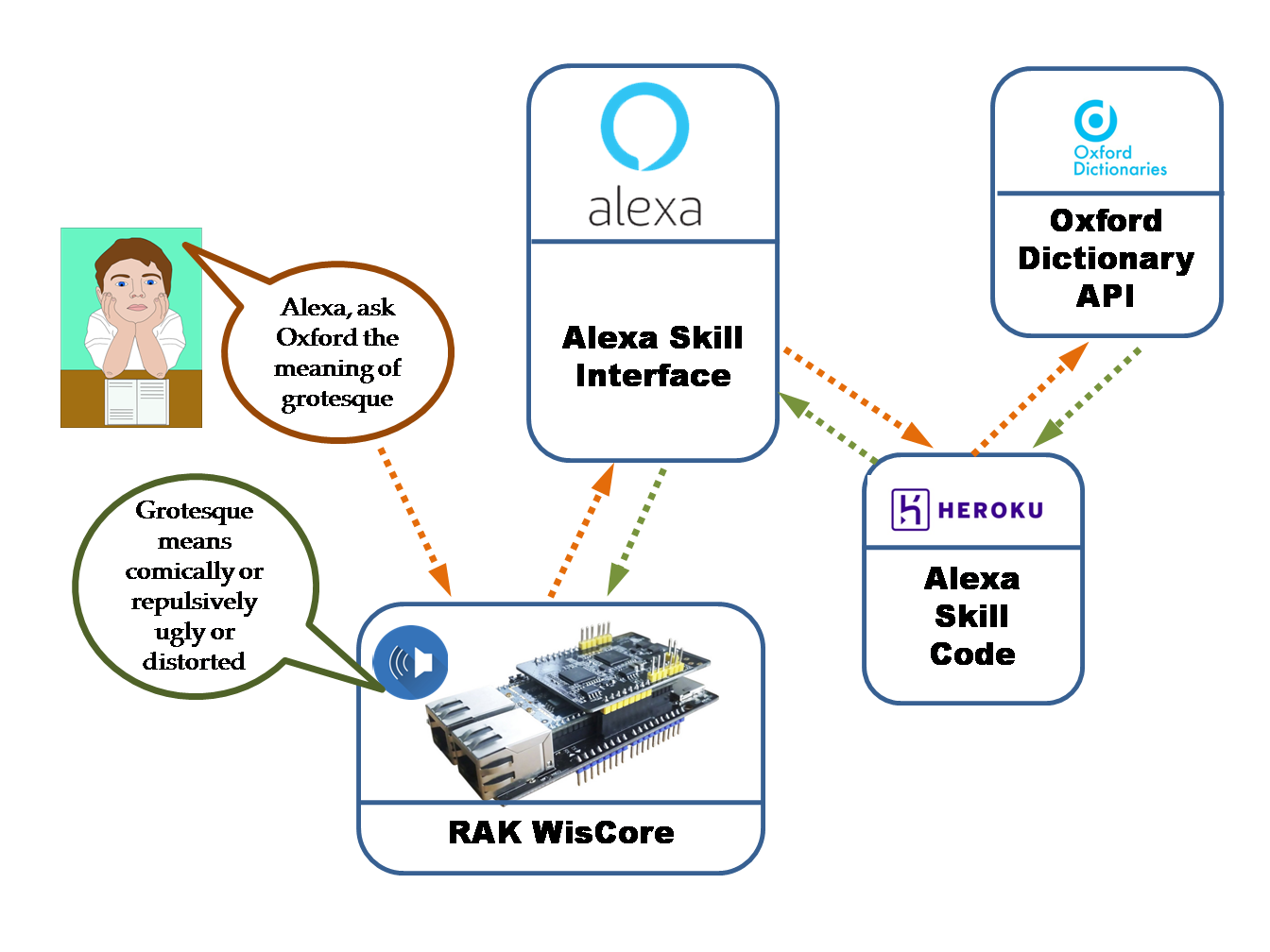
This image shows the architecture of our voice controlled talking dictionary application. In addition to Alexa voice service, we will use Heroku web service to host the skill code. The most important component of this system is the Oxford Dictionary API. Here is a brief description of these components to get you familiarized.
Oxford Dictionary API
Every one of us at some point has used an Oxford dictionary, though in a physical form. But what makes our voice-controlled dictionary bot possible is the online presence of this dictionary with an easy to use API to access its contents. You can simply query the dictionary and retrieve tremendous information about the English language including grammar and word origins as well. The API calls return information in a friendly JSON format so you can use the programming language of your choice. Oxford provides code snippets for Python, Java, Swift and Objective-C. You can get more details about the API and its capabilities here.
Heroku
Heroku is a great platform to build, deploy and manage web apps. The orchestration code for Alexa skill needs to be hosted as a web service since Alexa can’t access your local code. The web service should provide an https endpoint which needs to be configured in the Alexa skill. We will use Heroku to host our Alexa skill code. Heroku offers an easy interface to manage a web app and it supports various programming languages such as node.js, python, ruby etc. Heroku runs the app inside smart containers in a fully managed runtime environment so all you need is to push your code via GIT to the Heroku server.
Dictionary Bot in Action
Let’s get straight to see a demo of our voice activated Oxford dictionary.
[vimeo 248543506 w=640 h=360]
Here is a brief about what happens behind the screen when you use the voice-activated oxford dictionary bot.
- Wiscore runs a wakeword engine which keeps scanning your speech for the wakeword – ‘Alexa’.
- Once the wakeword engine detects this wakeword, it transfers the further speech to Amazon so the Alexa voice service can decode it and act accordingly.
- When you say, “Alexa, ask Oxford the definition of vivid‘, Alexa voice service interprets that this request is for a skill named ‘Oxford’.
- It then parses your speech into intent (Asking for definition) and slots (the word ‘vivid’) and passes these to our skill endpoint which is the app running on Heroku.
- The skill code running on Heroku web service, in turn, calls appropriate API from Oxford dictionary to retrieve the definition of word vivid.
- The skill code then parses the JSON data received from Oxford. It converts the parsed data into a meaningful sentence which forms the speech to be passed back to WisCore. Using SSML tags, it also adds expressiveness to the speech.
- Finally, the skill code passes back the resulting speech to WisCore which you hear from the connected speaker.
Note: The skill code speaks out how many definitions it found in the oxford dictionary and tells you all the definitions along with an example usage as well. You can further customize the code to speak more or little of the data returned by Oxford dictionary API.
Let’s Build The Dictionary Bot
If you find this idea exciting, let’s go ahead and start building the voice-controlled dictionary bot. Entire source code and instructions to build this app are provided on Github. Follow the instructions provided in the README file to build this talking dictionary yourself.
Here is an outline of the building process.
- Create required accounts
- Setup Wiscore AVS Kit
- Create and configure Alexa skill
- Create, configure and deploy Heroku web app
- Provide the Heroku endpoint to Alexa skill
- Enjoy talking to your Dictionary Bot
Conclusion
The voice-activated dictionary bot presented in this tutorial uses only a subset of the rich API provided by Oxford dictionary. There are numerous possibilities to extend the feature set and capabilities of this bot. A potential use case may be to develop a translation app of your own as Oxford provides translations to a few supported languages.
Additionally, you can think of leveraging the features of WisCore board. The hardware of WisCore features far-field recognition which means that you can talk to it from a distance of almost 15 feet. With multiple microphones, it can locate the direction of the sound as well. Moreover, it has got additional peripherals on board such as Ethernet, USB, UART, SPI, I2C and a number of GPIO pins. Together with Raspberry Pi or Arduino, you can develop rich voice-controlled products using WisCore.
So go ahead and have fun! Do let me know if you replicate this project and need any help.


