The Web3 ecosystem has experienced a sharp increase in spam NFTs and NFT phishing attacks. While such NFTs may seem benign – commonly used as promotions for new NFT collections – they can also be used as a method for duping unsuspecting users. Today, threat actors are using spam NFTs to drain wallets in a variety of ways. In this blog post, we take a closer look at some of these methods and the new security protections Fireblocks has developed to safeguard our customers.
This post was originally published in Fireblocks.
Use Case: NFT Phishing Attacks

Problem Statement
Web3 ecosystem is experiencing a sharp increase in NFT spams, with threat actors tricking unsuspecting users and draining their wallet balance in various ways.
Realization Approach
By combining an NFT library with a threat detection tool, it is possible to combat NFT phishing attacks by analyzing NFT transfers for spam or phishing behavior to safeguard a user’s NFT collection.

Solution Space
Through the security layer provided by the NFT library, a user’s NFT collection is protected by hiding spam NFTs and blocking any incoming spam NFT to avoid further operations on that NFT. In this way, users can secure and manage their NFT collections with advanced protection against spam and NFT phishing attacks.
Spam NFTs function similarly to the spam emails that clutter our inboxes. A spam email may tell you that you need to log into your bank account to verify a charge, but when you click on the link, you are actually directed to a phishing website that steals your login information. With spam NFTs, you may be directed to a dApp to claim a reward, but when you connect your wallet, the malicious smart contract drains funds from your wallet.
NFTs have become one of the primary mediums in crypto for spam and phishing because it’s easy for promoters and threat actors to utilize associated metadata, text messages, and images to influence users into taking a desired action.
4 Common NFT Phishing Attacks To Watch For
Promotional NFTs
Marketing for a New NFT Collection
NFT teams airdrop NFTs to a set of randomized wallets as a marketing tactic to promote a new NFT collection.
Fake NFT Collections
NFT teams airdrop NFTs to give a false perception that a collection has active wallet users – this tactic is commonly deployed by teams who intend to mislead users into purchasing an “active” collection.
Phishing NFTs
Phishing Collection Names
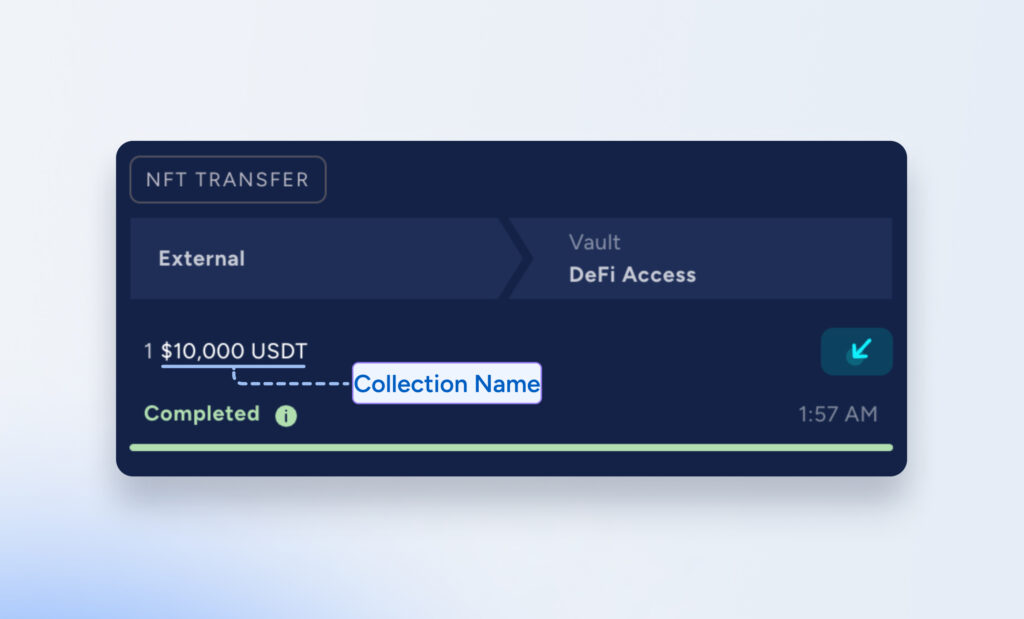
Threat actors contaminate a user’s transaction history by naming an NFT – for example, “$10,000 USDT” – and transferring the NFT to a user’s wallet. Unsuspecting users who quickly copy and paste addresses, believing the address resembles that of a trusted counterparty from their transaction history, are tricked into transferring tokens to the attackers’ wallet.
Phishing Airdrops
Threat actors leverage the NFT image and metadata text to display a message that misleads a user into visiting a phishing website. There are three common type of NFT phishing airdrops:

Redeemable Tokens or NFTs
The NFT metadata directs a user to a phishing website that tricks them into connecting and granting wallet permissions to a malicious smart contract in order to claim a reward. The malicious smart contract then proceeds to drain the funds in their wallet.
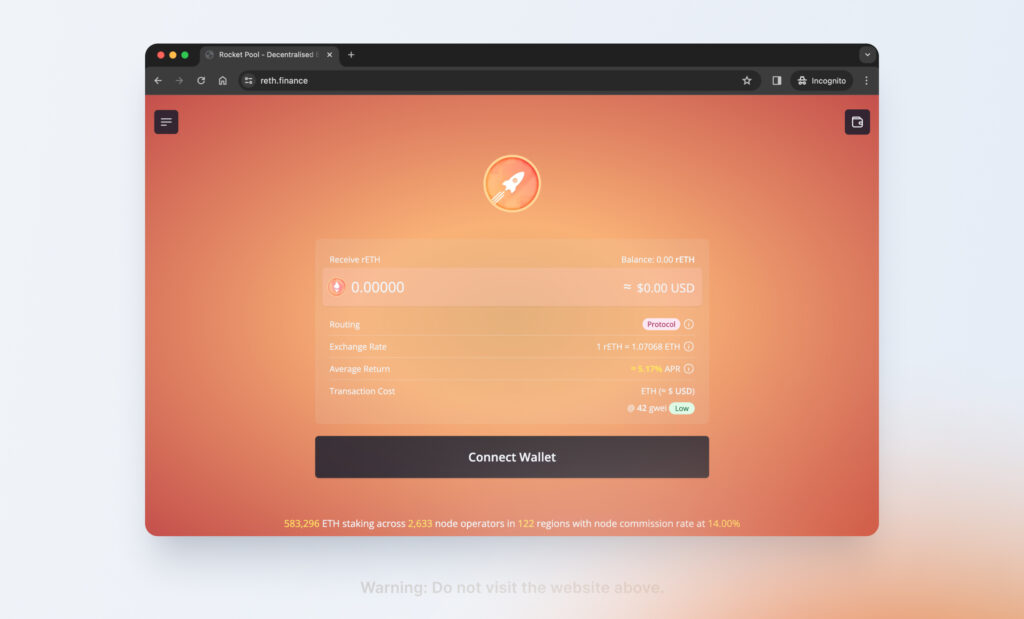
Phishing dApp
The attacker uses the NFT metadata to impersonate a legitimate dApp. In the example above, the attacker is impersonating RocketPool and instructs the user to access RocketPool via “www.reth.fi,” a phishing website that copies the front-end of RocketPool to trick users into believing that they are interacting with a legitimate dApp. The user then connects their wallet to a malicious smart contract and their wallet funds are drained.
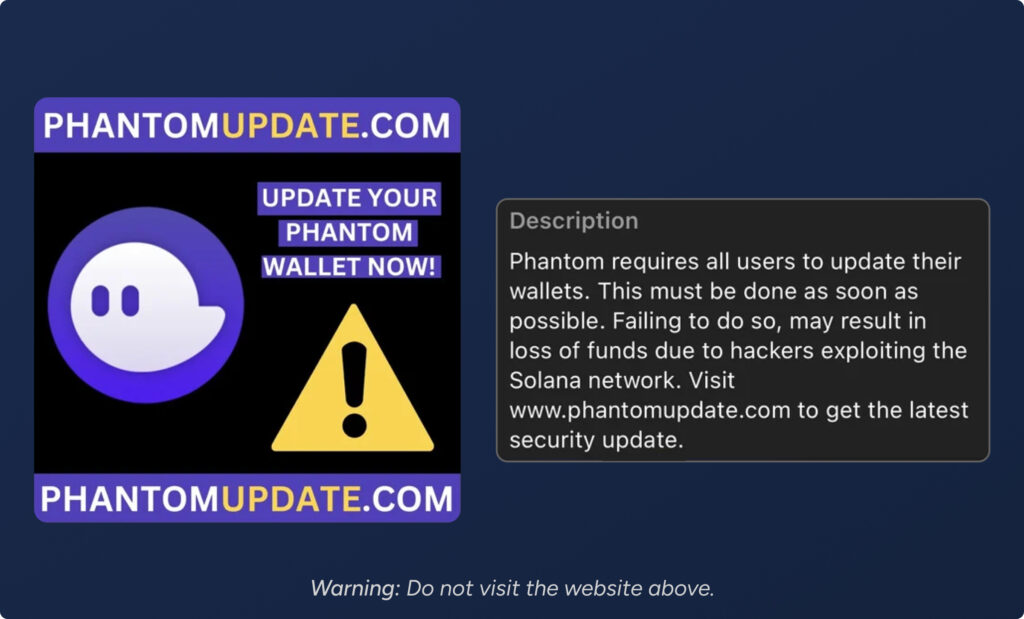
Malicious Software
The user is instructed to download a browser extension or software update in order to claim a reward or update their wallet. In the example above, an attacker airdropped an NFT to Phantom wallet users, instructing them to visit a phishing website and update their wallet security. Unbeknownst to the user, the downloaded software contains malware that drains any wallet that the user has on the compromised device.
Protecting Users From NFT Phishing Attacks
Fireblocks introduced the NFT Library early last year, simplifying NFT management for customers with an intuitive dashboard in the Console to manage their collections. As more customers began to manage their NFT collections through the Fireblocks Console, we noticed a rise in spam NFTs.
Fireblocks analyzed all owned collections among our users on Ethereum and Polygon. 82% of NFTs in these collections were identified as spam. Upon further observation, we noted that 87% of the collections on Polygon and 47% on Ethereum were spam. This difference might be attributed to the higher gas fees on Ethereum, which discourages spam activity.
The majority of spam NFTs analyzed were airdropped to customers for promotional purposes, cluttering their NFT Library and impacting the user experience. However, some of these spam NFTs also represented phishing attempts by threat actors.
We analyzed NFT airdrops on Fireblocks that contained attributes of phishing, such NFT collections that included popular tokens in the collection name and metadata that instructed users to visit a website to claim rewards. Fireblocks identified that 19% of NFT airdrops were part of an phishing collection name attack and 9% of NFTs were attributed to phishing websites that attempt to mislead users into connecting with a malicious dApp.
Fireblocks NFT Spam Protection
With security at our core, Fireblocks is constantly advancing our security posture to protect customers from emerging attack vectors. To combat the rise in spam and NFT phishing attacks, Fireblocks developed NFT Spam Protection – a new threat detection tool that automatically analyzes incoming NFT transfers and detects spam and phishing behavior. NFT Threat Protection leverages Blockaid, a Web3 threat intelligence platform, to detect malicious dApps and tokens. Here’s how it works:
When customers receive an NFT, Fireblocks automatically analyzes the NFT for characteristics commonly associated with spam, such as:
- Low-value or mass-produced collections
- Unverified creators or marketplaces
- Repetitive or nonsensical metadata
- Suspicious transaction patterns
If Fireblocks detects that an NFT exhibits spam indicators, the NFT is automatically marked as spam and hidden from customers’ NFT Library. Fireblocks also excludes incoming spam NFTs from being displayed in the Active Transfers panel to prevent displaying misleading token from spam NFTs.
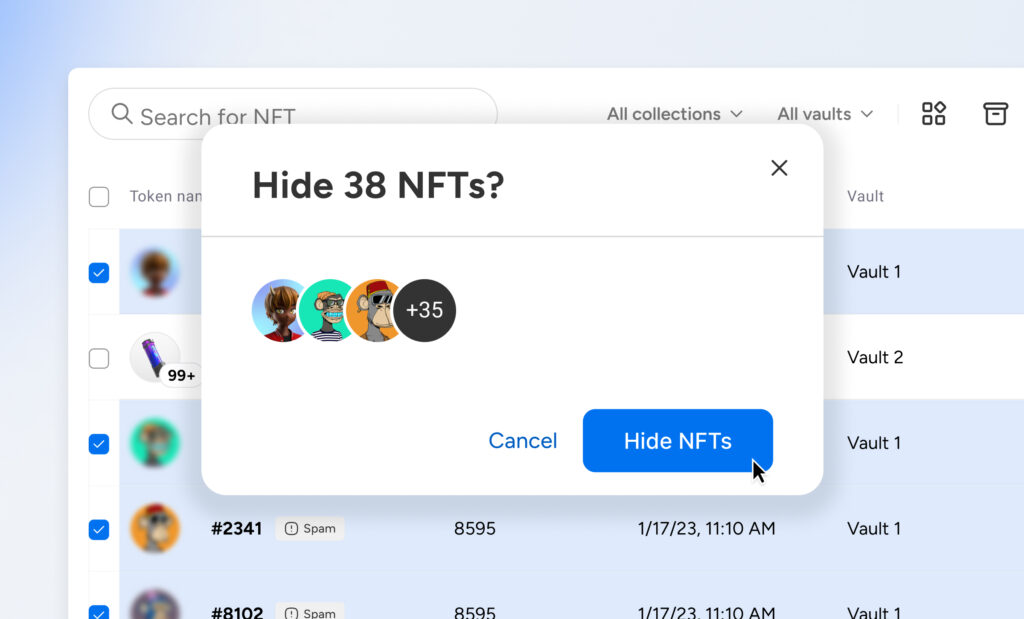
Customers can also mark individual NFTs as spam in their NFT Library to hide unwanted NFTs from the dashboard. Hidden NFTs remain accessible in the NFT Library but are not displayed in the main NFT collection view.
With the Fireblocks’ new NFT Spam Protection, customers are now able to secure and manage their NFT collections with advanced protection against spam and NFT phishing attacks.


