Cloud integration is the seamless connection and coordination of diverse software applications, data, and services across multiple cloud platforms, enhancing efficiency and facilitating digital transformation within an organization. But as simple as it may sound, a connection and coordination can quickly fan out into a big mess across many applications, micro services and cloud platforms.
This post was originally published in Digibee.
Use Case: Cloud Integration

Problem Statement
Businesses are always in a need for integrating their cloud hosted applications with third-party software, data and services across multiple cloud platforms. Without proper planning and strategy, it can lead to many issues related to interoperability, as well as scalability and security.
Realization Approach
A centralized cloud integration infrastructure which transforms siloed integrations into a managed, developer friendly, integration process and can also connect legacy on-premises applications with more modern cloud solutions.

Solution Space
An iPaaS driven approach to unify all cloud integrations to ensure end-to-end application and data integration, while also ensuring regulatory compliance. Overall, it optimizes workflows and business processes. resulting in flexibility, cost savings, and scale.
It is a crucial part of scalability – connecting a complex ecosystem of enterprise applications and data in a hybrid or multi-cloud environment. Businesses implement cloud integration projects to eliminate silos, optimize workflows and business processes, and connect difficult on-premises applications with more modern solutions.
A cloud integration initiative refers to both integrating applications and facilitating the real-time flow of data through legacy and cloud-based systems. Concepts related to cloud integration include cloud orchestration, cloud data integration, hybrid integration, and iPaaS.
The hallmarks of a successful cloud integration project are interoperability, visibility, scalability, and security. While some companies struggle to attain this in a cost-effective way, others leverage modern integration platforms to connect all their applications, keep data safe, and keep developers focused on high-value work.
What is Cloud Integration?
Enterprise cloud integration is the process of connecting various legacy and modern applications, data sources, and services into a single cloud-based or hybrid ecosystem. It’s typically the job of integration architects and engineers who help develop a digital transformation strategy, select an integration platform, and oversee the process of migrating and connecting data in the cloud.
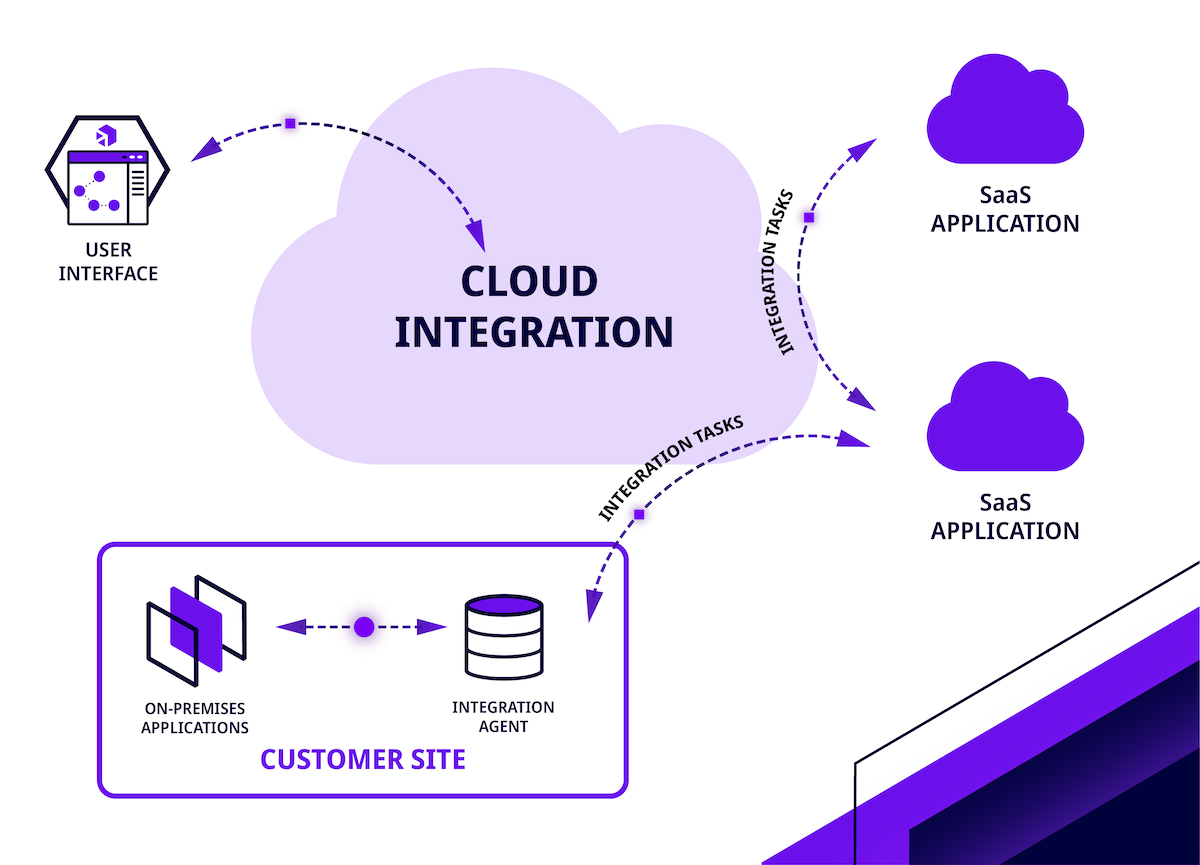
While some cloud integrations only connect cloud applications, most enterprise initiatives involve a blend of legacy applications, on-premises systems, SaaS solutions, and dozens of different micro-services and business tools. IT teams must strategically select technology to integrate, consider how they’ll protect sensitive data and comply with regulations, and decide how they’ll manage their integration processes as business needs evolve. A successful cloud integration lets companies transform their architecture, streamline operations, and act on real-time data while protecting sensitive information and keeping costs manageable.
What are the Different Types of Cloud Integration?
The term cloud integration may refer to several combinations of deployments and solutions. Some companies choose a hybrid deployment that keeps sensitive data on-premise but allows systems to interact with cloud applications for streamlined workflows. Others deploy fully in the cloud, using APIs and connectors to integrate apps and analyze real-time data in modern BI tools.
Cloud integrations generally fall into two types:
Application Integration
The first, application integration, is the process of connecting applications via native integrations, reusable components like connectors and accelerators, or APIs. These methods vary based on the company’s architecture choices and how applications need to interact. Application integration allows an action in one application to trigger a workflow in another, enabling automation, connectivity of business applications, and operational efficiency.
Data Integration
The second aspect of cloud integration is data integration, or the process of connecting multiple sources and enabling the real-time flow of data across the organization. Companies can collect data from integrated applications, pipe it to cloud-based data warehouses and tools, and analyze it in BI platforms. This helps companies improve data management, improve consistency by eliminating data silos, and empower teams to make data-driven decisions.
Because cloud integration involves multiple environments, tools, and data sources (and is critical to each team’s success), it’s important that developers, data experts, and integration architects collaborate to align on each dimension of a cloud integration initiative.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Integration?
A well-implemented cloud integration brings siloed, complex systems into one interconnected ecosystem. Companies that successfully integrate legacy solutions and connect data across all of their tools gain full visibility into the business, optimize costs, and scale quickly.
Here are Some of the Top Benefits of Cloud Integration:
Visibility and transparency
Cloud integrations connect and standardize data from both legacy systems and newer cloud applications. With a single source of truth, data teams can run deep analysis, create dashboards and reporting in a BI tool, or build self-service products that non-analysts can use to get answers on the fly. When everyone works from the same data, not in data silos, decisions are made quickly and confidently.
Efficient, automated workflows
When applications are integrated in the cloud and data flows freely without a burden on resources, many manual processes can be eliminated. Developers can use APIs to connect new tools quickly and experiment with automation, creating new scalable workflows. A single enterprise workflow improvement, like automating invoice creation based on a purchase order in an ERP, can almost instantly cut costs and improve cash flows.
Cost savings and ROI
Not only does cloud integration reduce cost by enabling automation, it also reduces IT overhead. Instead of maintaining legacy integration flows and adding to the backlog with every adjustment, engineers can modernize their architecture and free up time for core development projects. See an example in this Bauducco case study.
Scale
Many companies develop cloud integrations on modern, containerized infrastructure that auto scales as capacity needs change. This approach eliminates the need for running time-intensive batch processes, mitigates the lag associated with legacy databases, and circumvents the constraints of rate limits on app functionality.
Flexibility
Today’s cloud integrations are built using modular, composable architecture. This makes it easy to add or replace tools, quickly respond to stakeholder requests for things like dashboards, reports, and automations, and still keep data sets and systems safe and compliant.
Stay competitive
Integrating applications and data in the cloud gives organizations a competitive edge. They can better serve customers with high-quality support, adopt the latest in AI and automation tools, and rapidly deploy products and services in response to market demands.
What are the Challenges Associated with Cloud Integration?
While some businesses try to build an integration solution in-house or remain on legacy on-premises applications, such as a legacy iPaaS, these choices cause several problems. Cloud integration isn’t a one-time task, but rather an ongoing initiative that requires oversight to ensure data security, maintain compliance, and make continuous improvements as technology evolves.
Below are some of the biggest challenges that accompany a cloud integration project:
Painful implementation
Some cloud integration solutions can take over a year to fully implement, with tedious training requirements and costly service add-ons from providers. As you start your digital transformation initiative, look for integration tools that are easy for any developer—not just integration experts or certified platform specialists—to onboard quickly.
Rapid change
Cloud applications are frequently updated, acquired, replaced, and refactored, all changes that are difficult to keep up with if you’re managing legacy integration flows with existing on-premises systems. Developers should consider what happens in these scenarios and how they’ll avoid downtime and performance issues as they update any custom integrations.
Tedium and technical debt
Some companies try to build their own solution instead of adopting a platform built for cloud integrations. This approach isn’t scalable—each integration flow takes a long time to build and maintain, infrastructure must be managed in-house, and each new stakeholder request adds so much to the engineering backlog that ROI is hard to realize.
Security and compliance
Cloud integration moves large data sets across many platforms. Without the right security controls in place, this increases the risk of exposing sensitive information or non-compliance with industry or regional regulations like HIPAA, PCI, or GDPR. Modern cloud integration platforms are built on best-in-class infrastructure and include governance and security controls, but attempting this on your own may increase your attack surface or lead to fines.
How can iPaaS help with Cloud Integration?
The most efficient, scalable way to realize a cloud integration project today is with an integration platform as a service, or iPaaS. An iPaaS is a platform developers use to build and manage integrations on scalable architecture—it replaces outdated integration options like ESB and includes features like reusable components, a low-code interface, managed infrastructure, prebuilt integrations, and enterprise support.
Unlike some of its predecessors, Digibee’s iPaaS doesn’t require specialized training or a long implementation. On the contrary, it speeds up digital transformation projects by automating and simplifying the development workflows needed to connect legacy enterprise solutions and cloud applications in one ecosystem.
Digibee is different in that it is the only integration platform that scales application integration workflows while reducing cost, technical debt, and the burden on development teams. It allows developers to quickly build, test, deploy, govern, and monitor integrations across on-premises systems and cloud environments—they can then use the platform in tandem with API management and ETL tools for full synchronization across the organization.
What makes Digibee the right enterprise integration platform for your cloud integration initiative?
- A simple but powerful low-code interface speeds up workflows and empowers general developers to build integrations.
- Digibee Capsules replace connectors with modular, reusable components that provide greater flexibility.
- The platform is run on Kubernetes to leverage self-healing, autoscaling, and load-balancing capabilities that ensure high availability.
- Developers can test and monitor all of their integrations from a single, real-time dashboard.
- Digibee includes pre-built integrations for solutions like AWS and Salesforce.